Ovarian cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the egg or ovarian cells. Ovarian cancer is dangerous because it is difficult to detect in its early stages, making it sometimes known as the “silent killer.” In this article, we will take an overview of ovarian cancer, starting with the causes and factors affecting its development, to symptoms, diagnostic methods, and available treatment options.
What is ovarian cancer?
Definition of ovarian cancer:
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cells that make up the ovary. Ovarian cancer is the sixth most common cancer among women, and poses a major risk to women’s health.
Causes and risk factors for ovarian cancer
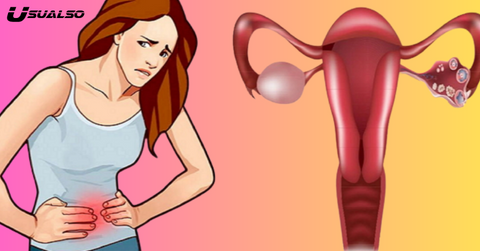
Risk factors:
Risk factors for ovarian cancer depend on a variety of genetic and environmental factors, including:
Genetic factors:
If there is a family history of ovarian cancer, your risk of developing it may increase significantly. Women who carry mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes have a significantly higher risk of developing ovarian cancer.
Age
The risk of ovarian cancer increases with age, especially after the age of fifty.
History of infertility and childlessness:
Childless women who have delayed childbearing have a higher risk of developing ovarian cancer.
Use of hormone therapy:
Some forms of hormone therapy used to treat infertility problems or menopausal symptoms can increase the risk of ovarian cancer.
Smoking:
There is some research that suggests that smoking may increase the risk of ovarian cancer.
Environmental factors:
Exposure to hazardous chemicals or radiation may increase the risk of ovarian cancer.
Signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer: